22365
  This is the 1647th original issue of Vernacular Blockchain Author | Terry Produced | Vernacular Blockchain (ID: hellobtc) The pledged amount of Ethereum 2.0 exceeds 12.6 million, a record high: According to reports on May 16, data from the analysis platform Nansen shows that the pledged amount of Ethereum 2.0 has exceeded 12.6 million, accounting for 10.4% of the total circulation, setting a record high. The amount of Ethereum pledged on the Lido platform exceeds 4.1 million, accounting for 32.5% of the total pledged amount of Ethereum 2.0, which is also a record high. On March 26, Ethereum core developer Tim Beiko summarized the contents of the latest core developer meeting, including the progress of the merged test network Kiln, difficulty bomb, Shanghai upgrade, Ethereum execution layer work progress, etc.  On April 13, Ethereum merger leader Tim Beiko responded on social media: The Merge will not be completed in June and is expected to be completed within the year. This not only means the real transformation of Ethereum from PoW to PoS, but also means that the so-called "Ethereum 2.0" is accelerating. 01 What is The Merge? Just in January this year, the Ethereum Foundation announced that in order to prepare for the merger, the expressions "Ethereum 1.0" (ETH1) and "Ethereum 2.0" (ETH2) will be eliminated and replaced by the "execution layer" and "consensus layer." There is no doubt that this is making final normative literal preparations for the arrival of Ethereum 2.0.  In early December 2021, Vitalik Buterin published an article titled "Endgame", proposing the eventual integration of all blockchains in the future, and also listed tools that allow block verification to occur in a decentralized and censorship-resistant manner. In short, Ethereum's beacon chain currently runs separately from the main network. Although the beacon chain runs in parallel using the PoS consensus mechanism, the current Ethereum main network continues to be protected through the PoW consensus mechanism. The Merge is the final integration of these two systems - when ready, the Ethereum mainnet will merge with the beacon chain, and the mainnet will introduce the ability to run smart contracts as well as the complete history and current status into the PoS system. That is, after the merger, existing Ethereum mainnet clients ("execution clients") will continue to host the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), and verify and broadcast exchanges, but will stop participating in proof-of-work (PoW) mining and relinquish responsibility for reaching consensus on the blockchain chain header (top block). Instead, this consensus will become the responsibility of the "consensus client", which is responsible for packaging the exchanges from the "execution client" together with the information required for consensus into "beacon blocks", and these beacon blocks form the beacon chain. “"Miners" will be replaced by "validators", who need to deposit ETH into an Ethereum smart contract (i.e. stake): The ETH staked by validators will serve as collateral to incentivize them to complete the verification work correctly. Validators who do not perform verification work (for example, because they are offline) or conduct malicious behavior will cause part of their staked ETH to be destroyed. On the other hand, if the validator behaves appropriately, they will be rewarded with ETH. This marks the end of the Ethereum PoW consensus mechanism, and also means that once the merger occurs, stakers will verify the Ethereum main network. The entire Ethereum network no longer requires GPU mining, and previous miners may invest in the new PoS system. 02 What are the possible impacts of The Merge? According to an information session hosted by ConsenSys, three researchers working on merging technologies believe that the merger of the Ethereum mainnet and the PoS beacon chain will reduce network energy usage by at least 99.95%. The blockchain consists of three parts: consensus layer, execution layer and data availability layer. The merger is an upgrade to the consensus layer, but the gas fee is paid to the execution layer. This means that The Merge will change the PoW consensus to POS, and the PoW chain will not produce new Ethereum. The new Ethereum will only be produced from PoS, which will reduce energy usage but will not affect Gas costs. According to current data estimates, after Ethereum switched to the PoS mechanism after The Merge upgrade, the number of new Ethereums added to PoS every year is about 600,000. However, according to the on-chain destruction data after the Ethereum to London upgrade in 2021, it is expected that the number of Ethereum destroyed due to EIP-1559 in a year is about 4.7 million. This means that from now on, the net destruction of Ethereum will be greater than the net output, which is -4.1 million. Combined with the current number of Ethereum of approximately 120 million, Ethereum will not only not be issued additionally every year, but will also be in a state of deflation: (0.6M POS - 4.7M burn)/118M = -3.5% This will undoubtedly provide strong support to prices from the supply side. At the same time, with the advancement of Eth2 and the imminent implementation of the London upgrade, facing the expectation of destruction, coupled with the demand for PoS, ETH will undoubtedly become more scarce, which is the most powerful boost to currency prices at the demand level. At the same time, although the current staking APR is about 4.5%, and the income will continue to decline as the total number of ETH pledges increases, Jacob Franek, a core contributor to the Web3 startup accelerator Alliance, recently tweeted that Coinbase expects the ETH staking annualized rate of return (APR) to rise to 9-12% after the merger (The Merge).  In fact, from this perspective, the act of pledging at least 32 ETH to obtain rewards can be simply compared to "Ethereum graphics card mining" under the new situation - every 32 ETH can be compared to a mining machine, and the reward generated by staking is the mining output. 03 Ethereum staking track overview However, before participating in Ethereum staking, we need to clarify some unique mechanism designs in Ethereum staking, because this is directly related to the specific participation methods currently available on the market. At least 32 ETH. When participating in staking, you must deposit at least 32 ETH (or a multiple of 32) into the deposit contract, which is undoubtedly a high capital threshold for most users. ; Slash punishment. Slash penalty means that the pledged node is punished for not complying with the agreement (basically around the technical operation and maintenance level), that is, the money is deducted from at least 32 ETH pledged in the node. If the node's pledged ETH Token drops below 16 due to the accumulation of Slash penalties, the node will automatically withdraw from the network. ; It can be seen from the above that small amounts of ETH cannot participate, the technical threshold of verification nodes, and the liquidity of pledged tokens are issues that require direct attention when participating in staking. The targeted ETH staking services currently on the market can basically be summarized as "two categories and four models." 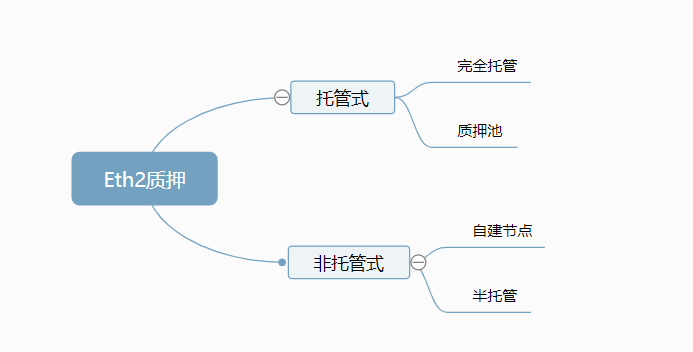
The biggest advantage of hosting is that it encapsulates the technical threshold of node construction and maintenance. Ordinary users don’t have to worry about hardware and software settings, Slash penalties, etc.
Non-custodial means decentralized, and the difference between it and custody is the difference between DEX and CEX, that is, the control of ETH assets is always in your own hands.
04 summary Overall, Vernacular Blockchain summarizes the respective characteristics and advantages of these "two categories and four models" as follows: 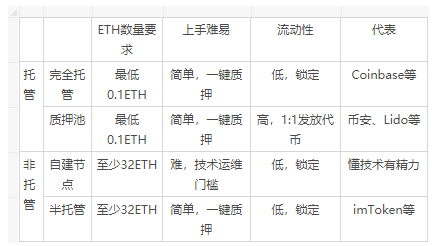 If I could sum it up in one sentence, it would be: For most ordinary users with long-tail needs, based on their professional technical capabilities and capital threshold restrictions, custody is definitely the first choice, and for liquidity considerations, pledge pool > full custody. In addition to long-tail demand, users with sufficient funds themselves do not have the technical strength and node operation and maintenance experience, so semi-hosted > self-built nodes; Even if you have technical strength and node operation and maintenance experience, from a cost perspective, it is still semi-managed > self-built nodes (of course, friends who are sentimental, regardless of cost, and not afraid of trouble will tell you otherwise). END Previous article: After the “bloodbath” of the Terra ecosystem, what impact will it have on the entire encryption field? Recommended reading Buterin: ENS is the most successful non-financial Ethereum application so far With countless auras above his head but extremely low valuation, is Ethereum, the "strongest killer", expected to be reborn? One article explains the largest second-layer network of TVL on Ethereum: Arbitrum Ethereum burned over 1 million after the London upgrade, is the Ethereum 2.0 staking track gradually clear? From giving up to really fragrant, the development puzzle of Ethereum behind Sanjian Capital’s big reversal of attitude 『Statement: This article is the independent opinion of the author and does not represent the position of vernacular blockchain. This content is only for popular science learning and communication among crypto enthusiasts. It does not constitute investment opinions or suggestions. Please treat it rationally, establish correct concepts, and improve risk awareness. The copyright and final interpretation rights of the article belong to Vernacular Blockchain. 』 If you like it, please click "Looking"👇 |