47145
 There is a group of people in the world for whom the Internet is a cash machine. Yes, it was then, and even more so now, because of the emergence of electronic money, the speed at which they withdraw money has become even crazier. In 2017, our honeypot detected a global large-scale attack on Ethereum, which we named the Ethereum "drive-by" vulnerability. Through this vulnerability, hackers can transfer all balances in the wallet without server permissions or keystore password permissions. Such a serious vulnerability was exposed on reddit.com a year ago and was being exploited by hackers. As early as February 14, 2016, hackers stole Bitcoin through this vulnerability: (https://www.reddit.com/r/ethereum/comments/4z0mvi/ethereum_nodes_with_insecure_rpc_settings_are/) Recently, China’s Slow Mist security team also exposed this attack method: (https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Kk2lsoQ1679Gda56Ec-zJg) For 2 years, not many users paid attention, and Ethereum did not take targeted protective measures. To this day, Ethereum's latest code is still not able to resist this attack. Therefore, we decided to make the detailed data we have available to everyone, hoping to prompt Ethereum developers to acknowledge and fix the vulnerability. Vulnerability causes(The following code analysis is based on the latest commit of https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum: commit b1917ac9a3cf4716460bd53a11db40384103e5e2)The most popular node programs in Ethereum (Geth/Parity) all provide RPC APIs for connecting to other third-party programs such as mining pools and wallets. By default, the node's RPC service can make interface calls without a password. The officially implemented RPC API does not provide the function of setting an RPC connection password. Therefore, once the RPC port is exposed to the Internet, it will be very dangerous. The Ethereum "smuggling" vulnerability we captured took advantage of Ethereum's default design of not authenticating RPC. Users who are attacked need to meet the following conditions: 1. The RPC port of the node is open to the outside world. 2. The RPC port of the node can directly call the API without additional authentication protection (such as authentication protection through nginx, etc.) 3. The block height of the node has been synchronized to the latest height of the network, because transfers need to be made at this node. If the highest height is not reached, the transfer cannot be made. When the user unlocks his wallet (unlockAccount function), during the unlock timeout period, he can call the eth_sendTransaction of the RPC API to perform a transfer operation without entering a password. The key components of the vulnerability are a combination of unauthenticated RPC API services and a certain password-free time after unlocking the account. The following is the unlockAccount function to unlock the account: Code path: go-ethereum/internal/jsre/deps/api.go 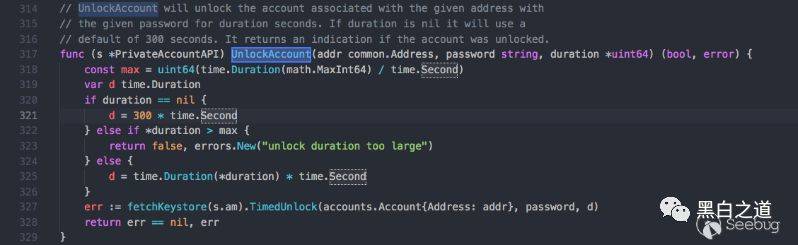 It can be seen from the implementation code of the function that the API for unlocking the account allows the timeout to be passed in. The default timeout is 300 seconds. The actual unlocking function TimedUnlock is implemented as follows: Code path: go-ethereum/accounts/keystore/keystore.go 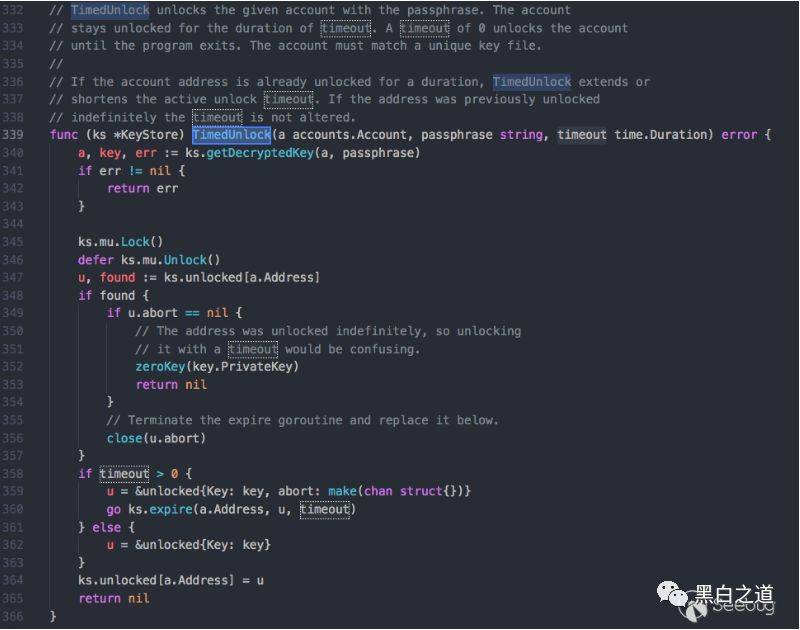 When the incoming timeout is greater than 0, a coroutine will be initiated for timeout processing. If the incoming timeout is 0, it will never time out and the account will remain unlocked until the node process exits. For detailed usage, please refer to the official documentation: https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/wiki/Management-APIs#personal_unlockaccount Attack techniques revealed1. Find a server that opens the Ethereum RPC port to the outside world and confirm that the node has reached the highest block height of the Ethereum network. When the hacker discovered through global port service scanning that the RPC service was the RPC interface of Ethereum, he called eth_getBlockByNumber('last', false) to obtain the latest block height. However, because some Ethereum nodes are forked coins of Ethereum and have different heights from Ethereum, hackers will not give up the attack even if they find that the height of the node is different from that of Ethereum. 2. Call eth_accounts to obtain all accounts on the node. The request for eth_accounts will return a list of account addresses: [0x1834axxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, 0xa13jkcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx,… ] 3. Call eth_getBalance to query the address balance. In this process, hackers can complete Ethereum balance inquiries on their own servers, because Ethereum's blockchain ledger database is freely available to the public. Some hackers have not set up a full node of Ethereum and have not checked the balance by themselves, so they will also perform the eth_getBalance operation on the attacked server. 4. Continue to call the transfer operation until the user unlocks the wallet with the password and completes the "smuggling" of the illegal transfer operation.” The hacker will construct the transfer operation of eth_sendTransaction and fill in the balance and fixed handling fee: {"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":2,"method":"eth_sendTransaction","params":[{"from":"Victim Wallet Address 1","gas":"0x55f0","to":"0xdc3431d42c0bf108b44cb48bfbd2cd4d392c32d6","value":"0x112345fc212345000"}]} {"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":2,"method":"eth_sendTransaction","params":[{"from":"Victim wallet address 2","gas":"0x55f0","to":"0xdc3431d42c0bf108b44cb48bfbd2cd4d392c32d6","value":"0x112345fc212345000"}]} {"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":2,"method":"eth_sendTransaction","params":[{"from":"Victim wallet address 3","gas":"0x55f0","to":"0xdc3431d42c0bf108b44cb48bfbd2cd4d392c32d6","value":"0x112345fc212345000"}]} The unit of value is the smallest unit of ether: wei. To calculate it as ether, you need to divide 10 to the 18th power: >>> 0x112345fc212345000 19758522752314920960L >>> 19758522752314920960L/1000000000000000000 19L The user uses the wallet and enters the password to unlock the wallet. At this time, the wallet balance will be transferred immediately. Rapid vulnerability testingInstall the python web3 library, then connect to the RPC port and initiate a request. If the return result is obtained, this vulnerability may exist.Reference: http://web3py.readthedocs.io/en/stable/quickstart.html from web3 import Web3, HTTPProvider, IPCProvider web3 = Web3(HTTPProvider(‘http://ip:port’)) web3.eth.blockNumber Hacker decryption and IOCs intelligencehacker walletAt present, we have the wallet payment addresses of 3 hackers, and the account balance that has not been transferred is 22.2 million US dollars: https://etherscan.io/address/0x957cD4Ff9b3894FC78b5134A8DC72b032fFbC464, the balance is 38,076 ETH (erc20 token is not counted), the earliest payment was 2016-2-14, and the latest payment is 2018-3-21 (currently the payment is still continuing) https://etherscan.io/address/0x96a5296eb1d8f8098d35f300659c95f7d6362d15, the balance is 321 ETH (erc20 token is not counted), the earliest payment was 2016-8-10, and the latest payment was 2017-11-28. https://etherscan.io/address/0xdc3431d42c0bf108b44cb48bfbd2cd4d392c32d6, the balance is 330 ETH (erc20 token is not counted), the earliest payment was 2018-2-06, and the latest payment was 2018-3-20. Hacker attack source IP146.0.249.87 (Frankfurt, Hesse, Germany) 162.251.61.133 (Canada) 190.2.133.114 (Curaçao) 85.14.240.84 (North Rhine, Germany) Currently, most hackers use https://github.com/regcostajr/go-web3 to make frequent API requests. If you see a large number of POST requests with user-agent "Go-http-client/1.1", please record the request content to confirm whether it is a malicious behavior. Emergency response and repair suggestions1. Close the RPC port exposed to the outside world. If it must be exposed to the Internet, please use authentication: https://tokenmarket.net/blog/protecting-ethereum-json-rpc-api-with-password/ 2. Use network protection software such as firewalls to block hacker attack source IP addresses 3. Check the RPC logs and web interface logs to see if there are an unusually large number of frequent requests. Check whether the request content is eth_sendTransaction. 4. Wait for Ethereum to update the latest code and use the node program that fixes the vulnerability. Author:Hydra@BLOCKCHAIN SECURITY LAB Author's blog: http://www.sec-lab.io/2018/03/21/ethereum-smuggling-vulnerability/  you may like An exciting night on March 7: See how hackers implement decentralized attacks  |